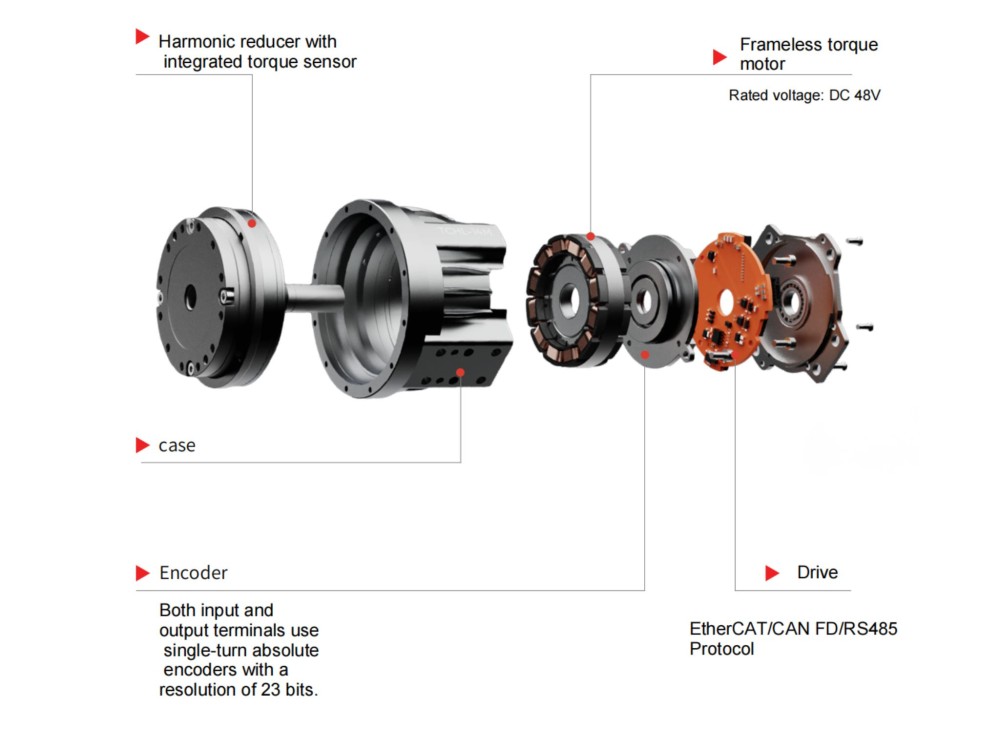
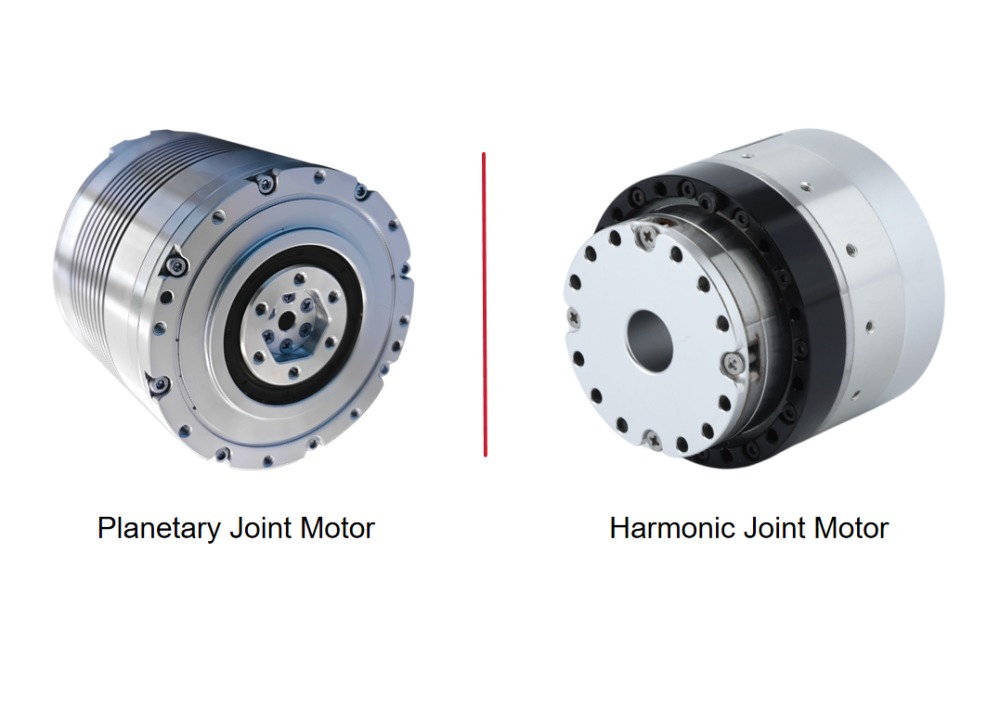
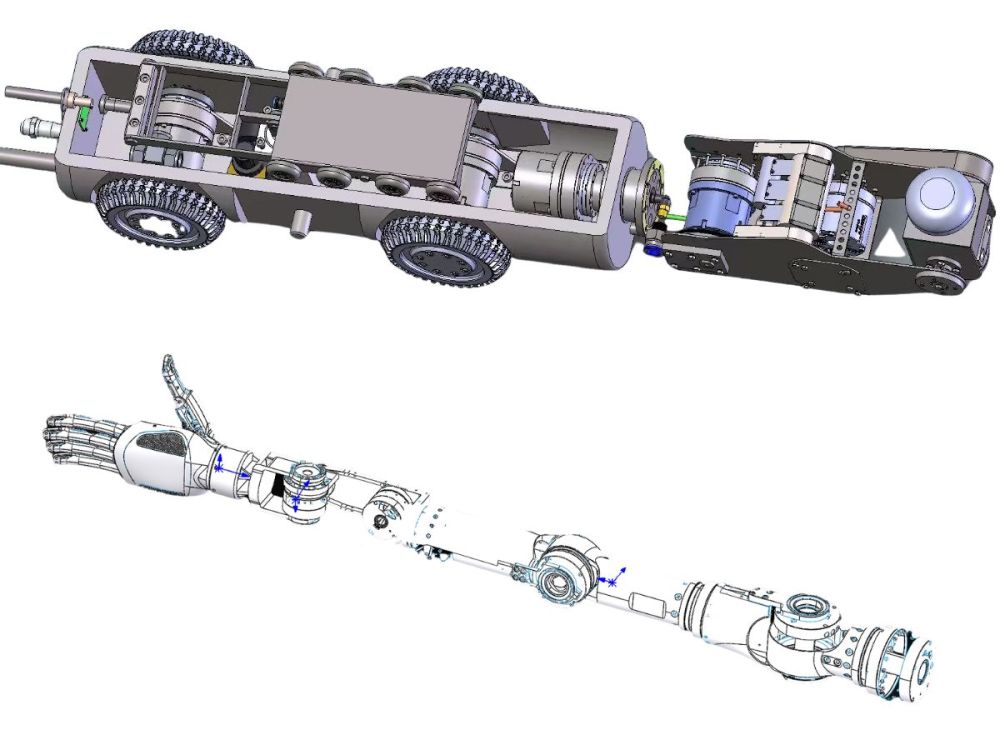
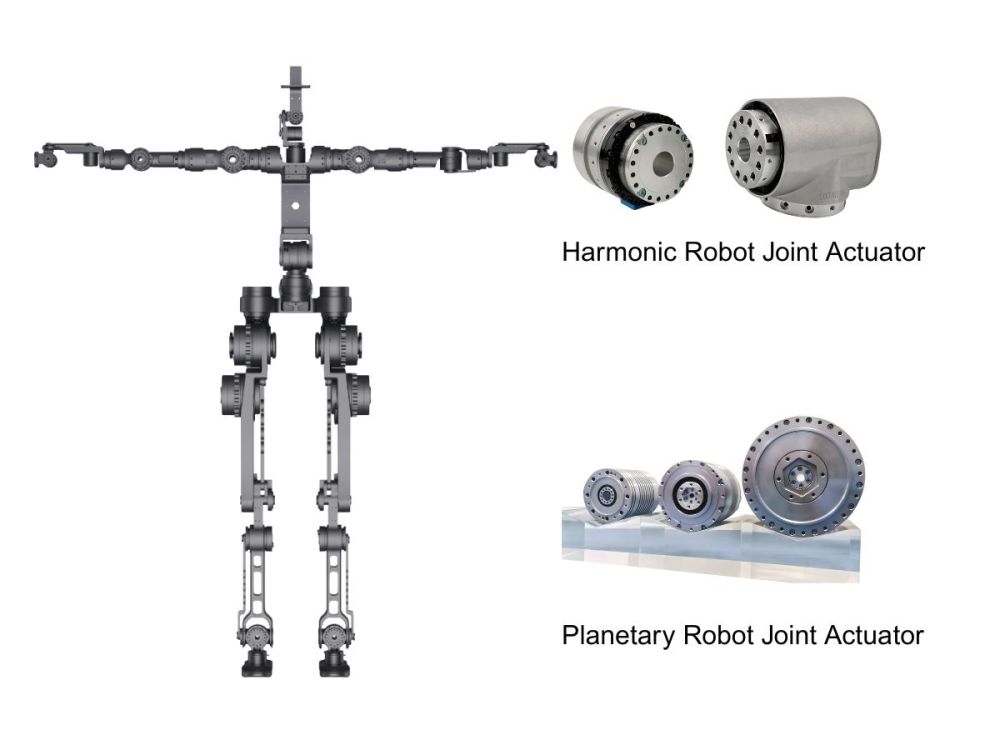
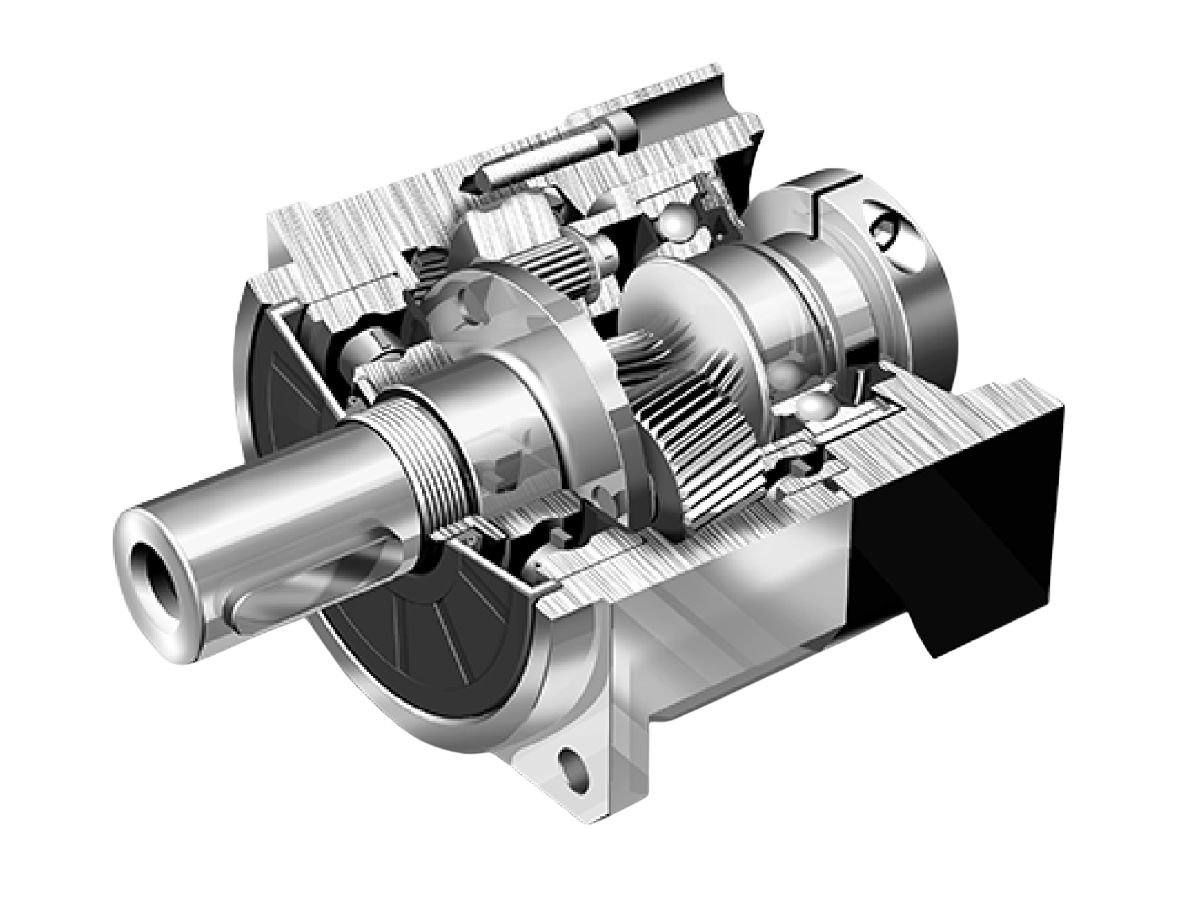
The Most Comprehensive Guide to Planetary Gearbox Selection and Common Pitfalls
As a “core link” in transmission systems, planetary gearboxes are widely used in automation equipment, robotics, conveyor lines, and many other applications.
When selecting a planetary gearbox, people usually first think of parameters such as output torque, speed and gear ratio, motor type, maximum output speed, backlash, torsional stiffness, service life, mounting method, and output configuration.
Based on many years of experience in supporting customers with gearbox selection, HONPINE has summarized a more in-depth guide and several common selection pitfalls to help users make more reliable and cost-effective decisions.
Planetary Gearbox Selection Steps
● Determine the torque and speed required by the load.
● Determine the overall speed ratio between motor speed and load speed.
● Determine the gearbox reduction ratio, as well as any additional reductions outside the gearbox (pulleys, chains, external gears, etc.).
● Determine the applicable service factor and overhung load (K) factor.
Calculate the actual required gearbox output torque, and select a gearbox with a Maximum Thermal Output Torque rating higher than this value
(applicable to WG cast-iron gearboxes; not applicable to WGA aluminum gearboxes).
● Determine the design output torque (actual torque multiplied by the service factor), and select a gearbox with a Maximum Mechanical Output Torque rating higher than this value
(the gearbox must also meet all other requirements).
● Determine the required sizes of pulleys, gears, and other transmission components, calculate the overhung load, and select a gearbox with a higher Overhung Load Rating
(the gearbox must also meet all other requirements).
● Confirm that the selected gearbox meets all system and application requirements.
Select a compatible motor.
Common Pitfalls in Planetary Gearbox Selection
Focusing Only on Gear Ratio While Ignoring Inertia Matching
The gear ratio only solves the problem of speed matching, while inertia matching directly determines the dynamic performance of the system.
In simple terms, inertia is an object’s resistance to acceleration. If the load inertia at the gearbox output is poorly matched with the motor’s rotor inertia, it is like a small horse pulling a heavy cart. The motor must generate extra torque to overcome inertia, resulting in slow response, poor positioning accuracy, and unstable operation.
Inertia matching must be verified:In general applications, the ratio of load inertia to motor rotor inertia should be kept within 5:1
For high-precision equipment, it should be controlled within 3:1
Calculation logic:Load inertia = (gear ratio)² × actual load inertia
(including workpieces, conveyor belts, and all moving components)
Ignoring the Safety Factor and Selecting Only Based on Rated Conditions
In real operating conditions, loads are rarely constant.
Start-up shocks, fluctuations in material weight, and unexpected jams can all cause the load to momentarily exceed its rated value.
If no safety factor is reserved, the gearbox will operate under long-term overload conditions, accelerating wear of key components such as gears and bearings, and significantly shortening service life.
The safety factor is not “waste,” but “insurance”:Based on load fluctuation characteristics, a safety factor of 1.2–2.0 should be reasonably applied.
Over-Pursuing High Precision and Causing Unnecessary Cost
The precision of a planetary gearbox (such as backlash and repeat positioning accuracy) is directly linked to cost.Each increase in precision grade can significantly increase manufacturing costs. However, not all applications require ultra-high precision.
Blindly pursuing high precision may result in:Unnecessary cost increases,Higher installation accuracy requirements,Increased maintenance difficulty and cost.
The core principle of precision selection:Match the actual control and positioning requirements, not “the higher, the better”.
Ignoring Installation Details and Creating Hidden Operational Risks
The installation accuracy of a planetary gearbox has a direct impact on its operating performance.
Shaft misalignment generates additional radial forces
Excessive axial forces place stress on bearings
Both conditions accelerate wear, increase noise, and may even lead to mechanical failure.
Key requirements:Ensure proper shaft alignment,Avoid excessive radial and axial loads
Recommended practices:Use a dial indicator during installation to verify alignment
→ Coaxiality error between the motor shaft and gearbox input shaft ≤ 0.02 mm
Avoid overly rigid connections; use flexible couplings to compensate for misalignment and reduce radial forces.Never strike the gearbox shaft during installation to prevent damage to internal gears and bearings
After reading this article, do you have a deeper understanding of planetary gearbox selection?
If you are looking for a high-precision planetary gearbox supplier, feel free to contact us.
We will provide you with the most comprehensive gearbox selection guidance tailored to your application.
Read More
Learn more about the story of HONPINE and industry trends related to precision transmission.
Double Click
We provide harmonic drive reducer,planetary reducer,robot joint motor,robot rotary actuators,RV gear reducer,robot end effector,dexterous robot hand